
يتضمن حساب متطلبات الطاقة لمصدر طاقة السكك الحديدية DIN تحديد إجمالي الطاقة الكهربائية التي يحتاجها نظامك ليعمل بشكل موثوق وفعال. يضمن هذا الحساب تصنيف مصدر الطاقة بشكل مناسب للتعامل مع متطلبات أجهزتك وأي تقلبات محتملة. فيما يلي دليل تفصيلي خطوة بخطوة لإجراء هذا الحساب.
1. فهم المعلمات الرئيسية
قبل البدء، تعرف على المصطلحات الكهربائية التالية وكيفية ارتباطها بمعداتك:
--- الجهد (V): الإمكانات الكهربائية التي تحتاجها أجهزتك للعمل. يتم قياس هذه القيمة عادةً بالفولت (V)، وغالبًا ما يتم تحديدها على ملصق الجهاز.
--- التيار (I): مقدار التيار الكهربائي الذي تستهلكه أجهزتك. يمكن أن يختلف هذا المقاس بالأمبير (A) اعتمادًا على تشغيل الجهاز.
--- الطاقة (P): إجمالي الطاقة المطلوبة، محسوبة باستخدام الصيغة P=V×I. يتم قياس الطاقة بالواط (W).
2. قم بجرد أجهزتك
قم بعمل قائمة بجميع الأجهزة أو المكونات التي سيتم تشغيلها بواسطة مصدر طاقة السكك الحديدية DIN. قم بتضمين المعلومات التالية لكل جهاز:
--- جهد التشغيل: متطلبات الجهد لكل جهاز.
--- تيار التشغيل : التيار الذي يسحبه كل جهاز في ظروف التشغيل العادية .
3. احسب إجمالي متطلبات الطاقة
الخطوة 1: تحديد الطاقة لكل جهاز
لكل جهاز، استخدم الصيغة:
ع=الخامس×أنا
مثال: إذا كان الجهاز يعمل بجهد 24 فولت ويستهلك 0.5 أمبير، فإن متطلبات الطاقة الخاصة به هي:
P=24V×0.5A=12W
الخطوة 2: جمع متطلبات الطاقة
--- قم بإضافة متطلبات الطاقة لجميع الأجهزة لحساب إجمالي الطاقة اللازمة للنظام.
مثال: إذا كان لديك ثلاثة أجهزة تتطلب 12 وات، و20 وات، و18 وات، فإن إجمالي متطلبات الطاقة هو:
إجمالي الطاقة = 12 وات + 20 وات + 18 وات = 50 وات
4. حساب خسارة الكفاءة
--- مصادر الطاقة الخاصة بالسكك الحديدية DIN ليست فعالة بنسبة 100%. وتتراوح الكفاءة النموذجية من 85% إلى 95%، اعتمادًا على الطراز والشركة المصنعة. لمراعاة ذلك، قم بتقسيم إجمالي متطلبات الطاقة على كفاءة مصدر الطاقة (معبرًا عنها بعلامة عشرية).
مثال: إذا كان إجمالي متطلبات الطاقة 50 وات وكفاءة مصدر الطاقة 90% (0.90)، فإن طاقة الإدخال الفعلية المطلوبة هي:
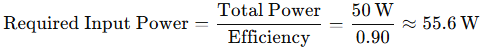
5. أضف هامش أمان
--- من الضروري تضمين هامش أمان للتعامل مع الزيادات غير المتوقعة أو تيارات بدء التشغيل أو التوسعات المستقبلية. هامش الأمان النموذجي هو 20% إلى 30% أعلى من إجمالي متطلبات الطاقة المحسوبة.
مثال: إذا كانت متطلبات الطاقة المعدلة هي 55.6 واط، فقم بإضافة هامش بنسبة 20%:
متطلبات الطاقة النهائية = 55.6 واط × 1.20 = 66.72 واط
6. اختر مصدر طاقة DIN Rail
--- حدد مصدر طاقة DIN للسكك الحديدية بمعدل خرج طاقة أعلى من متطلبات الطاقة النهائية. يتم تصنيف معظم مصادر طاقة السكك الحديدية DIN من حيث الجهد الكهربي وقدرتها الكهربائية، مثل 24 فولت، 100 واط.
--- مثال: إذا كانت متطلبات الطاقة النهائية لديك هي 66.72 وات، فسيكون مصدر الطاقة 24 فولت و100 وات خيارًا مناسبًا، لأنه يتجاوز متطلباتك المحسوبة.
7. التحقق من توافق الجهد
--- تأكد من أن جهد الخرج لمصدر طاقة سكة DIN يتطابق مع جهد التشغيل لأجهزتك. بالنسبة للأنظمة ذات متطلبات الجهد المختلط، قد تحتاج إلى مصادر طاقة متعددة أو محولات إضافية.
8. النظر في المتطلبات الخاصة
--- تيارات بدء التشغيل: قد تسحب المحركات والمرحلات وبعض الأجهزة الإلكترونية تيارات أعلى عند بدء التشغيل. تحقق من المتطلبات الحالية لبدء التشغيل وتأكد من قدرة مصدر الطاقة على التعامل مع الزيادات قصيرة المدى.
--- التكرار: إذا كانت موثوقية النظام أمرًا بالغ الأهمية، ففكر في استخدام مصادر الطاقة مع خيارات التكرار لضمان التشغيل المستمر في حالة الفشل.
--- العوامل البيئية: إذا كان مصدر الطاقة سيعمل في بيئات ذات درجة حرارة عالية، فضع في الاعتبار احتمال انخفاض القدرة الإنتاجية، حيث قد تنخفض سعة الإخراج في ظل الظروف القاسية.
حساب المثال
سيناريو:
لديك ثلاثة أجهزة بالمواصفات التالية:
--- الجهاز أ: 24 فولت، 1 أمبير
--- الجهاز ب: 24 فولت، 0.8 أمبير
--- الجهاز ج: 12 فولت، 2 أمبير
خطوات:
1. حساب الطاقة لكل جهاز:
--- الجهاز أ: 24 فولت × 1 أمبير = 24 وات
--- الجهاز ب: 24 فولت × 0.8 أمبير = 19.2 واط
--- الجهاز ج: 12 فولت × 2 أمبير = 24 وات
2. إجمالي الطاقة المطلوبة:
إجمالي الطاقة = 24 واط + 19.2 واط + 24 واط = 67.2 واط
3. ضبط الكفاءة (90%):
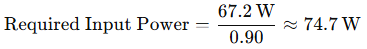
4. إضافة هامش أمان بنسبة 20%:
متطلبات الطاقة النهائية = 74.7 واط × 1.20 = 89.64 واط
5. حدد مصدر طاقة: اختر مصدر طاقة سكة DIN بقدرة 24 فولت و100 وات لتلبية هذه المتطلبات.
خاتمة
يتضمن حساب متطلبات الطاقة لمصدر طاقة السكك الحديدية DIN تقييم إجمالي احتياجات الطاقة للأجهزة المتصلة، وحساب خسائر الكفاءة، وإضافة هامش أمان. يضمن اتباع هذه الخطوات تحديد مصدر طاقة يوفر أداءً موثوقًا وفعالاً مع تلبية متطلبات النظام المحتملة.